Thermocouple Board (MAX6675)

The MAX6675 digitize and returns the readings from a type-K thermocouple using the SPI interface. Temperature resolution is 0.25C and readings can be as high as 1024C (...provided a suitable thermocouple is used).
This sensor is mainly used for measuring high temperature. For lower temperatures, other sensors like the DHT22 or DS18B20 are better choices.
Pins
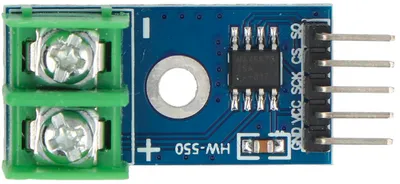
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Power for the sensor. Connect to 3V3. If your device is on USB power, you can also use VIN. |
| GND | Ground pin. Connect to the GND pin on the ESP32. |
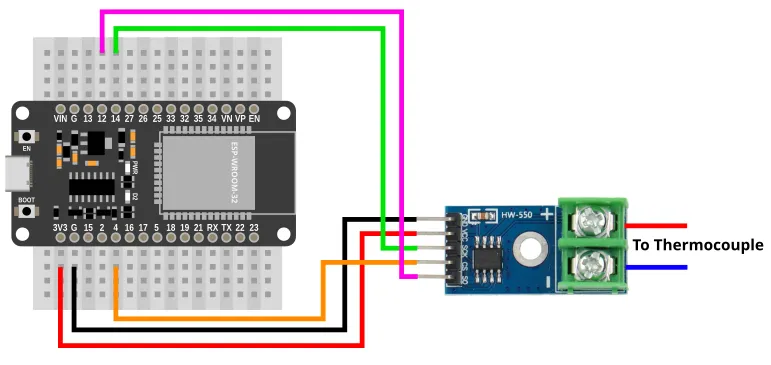
| SCK | Serial Clock. This is used to communicate with the ESP32 using the SPI protocol (default pin 14). |
| SO | Serial Out (aka MISO). This is used to communicate with the ESP32 using the SPI protocol (default pin 12). |
| CS | Chip Select. This is used to activate communication with the sensor. Connect to any output capable pin (default pin 4). |
| + (screw terminal) | Thermocouple +. Connect to the red lead of the thermocouple. |
| - (screw terminal) | Thermocouple -. Connect to the blue/black lead of the thermocouple. |
Wiring
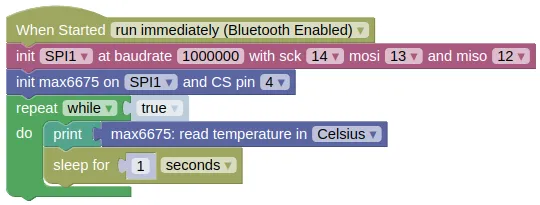
Code
This code will print the temperature readings.
Blocks
Python
import machine
import max6675
import time
spi1 = machine.SPI(1, baudrate=1000000, sck=Pin(14), mosi=Pin(13), miso=Pin(12))
max6675_device = max6675.MAX6675(spi1, 4)
while True:
print(max6675_device.read_celsius())
time.sleep(1)
Results
You should see the temperature readings printed in the monitor.
class MAX6675 - control MAX6675 thermocouple board
Constructors
max6675.MAX6675(spi, cs)
Creates a MAX6675 object.
The arguments are:
-
spiAn spi object. -
csAn integer representing the microcontroller pin connected to the CS pin on the sensor.
Returns a MAX6675 object.
Methods
MAX6675.read_celsius()
Get the currently stored temperature, then trigger a new reading.
Note that this returns the stored temperature (...which might be from a long time ago).
Returns a number representing the temperature in Celsius.
MAX6675.read_fahrenheit()
Get the currently stored temperature, then trigger a new reading.
Note that this returns the stored temperature (...which might be from a long time ago).
Returns a number representing the temperature in Fahrenheit.
MAX6675.read_kelvin()
Get the currently stored temperature, then trigger a new reading.
Note that this returns the stored temperature (...which might be from a long time ago).
Returns a number representing the temperature in Kelvin.
